How Diskless Boot Improves Performance in Gaming Centers

We’ve already talked about how diskless boot works in our previous blog, and you should have a general understanding of what it can do. A diskless boot system lets you run your server without requiring network or physical storage to operate.
Now in this post, we want to tackle one of the first questions that come to mind about this approach, “How does it fare in terms of performance?” and “Will it tax my gaming system or the server when I run diskless boot?”
Questions and Concerns Regarding Diskless Boot
At ggCircuit, we get a lot of questions on how diskless boot compares to physical hardware, and that’s understandable. Some of the most common queries are:
● Does diskless boot steal RAM?
● Does diskless boot require more CPU?
● Is there lag when using diskless boot?
We’re happy to say that the answer to these three questions is no, a preboot execution environment PXE boot doesn’t steal RAM, require more CPU, nor does it cause lag. In general it doesn’t perform worse than using physical hardware. In some cases it may even improve overall server performance in gaming centers since it uses RAM speed as its main drive.
Diskless boot abstracts your physical drives, such as your HDDs and SSDs, from your actual machine and creates virtualization of it on the boot server. You can think of it this way: your drives are connected to your motherboard through an Ethernet cable within a virtual drive.
Advantages of PXE Boot Over Physical Installation
Since connection to the dynamic host configuration protocol server (DHCP server) is done virtually, SATA links aren’t necessary with a diskless boot setup. This allows PXE boot to have several distinct advantages over a physical installation that makes it ideal to improve esports venue performance.
Sign up for ggCircuit Updates!
Comparable or Lower Latency Than a Physical Installation
On average, the diskless boot is often found to have comparable latency to local drives assuming that RAM cache is employed.
Obtaining data over the much shorter (and working through a different protocol) SATA cable is often faster in comparison to getting in through an Ethernet cable on the server, especially if it has its own SATA drives that house the virtual server. That said, if these drives have RAM cache available, the latency of a diskless boot would be comparable, or even lower, compared to a physical installation.
With lower latency, users can have the same or even better overall gaming experiences since the metrics will stay the same or improve marginally. It’s common to experience faster loading times for Windows startup, video games, and using other software.
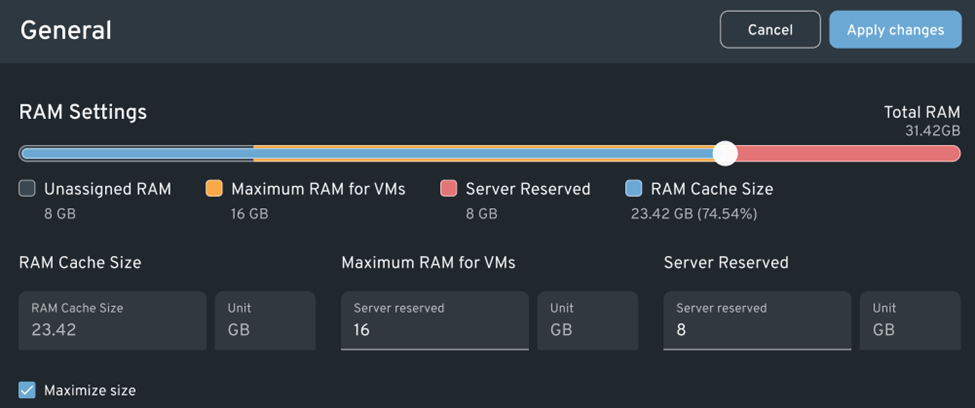
Diskless Boot Doesn’t Require Additional RAM, CPU, or GPU Resources
One of the biggest misconceptions about diskless boot systems is that they tax the performance of client machines by taking up valuable CPU, GPU, or RAM resources. This belief may have stemmed from misinformation passed on by those who think a diskless boot setup should have a major trade-off for the benefits it provides.
However, this is not the case with a diskless boot. The performance for the RAM, CPU, or GPU resources of a computer within a diskless boot system remains identical or even better than using physical hard drives.
Loading of Repetitive and Frequent Data Can Be Sped Up
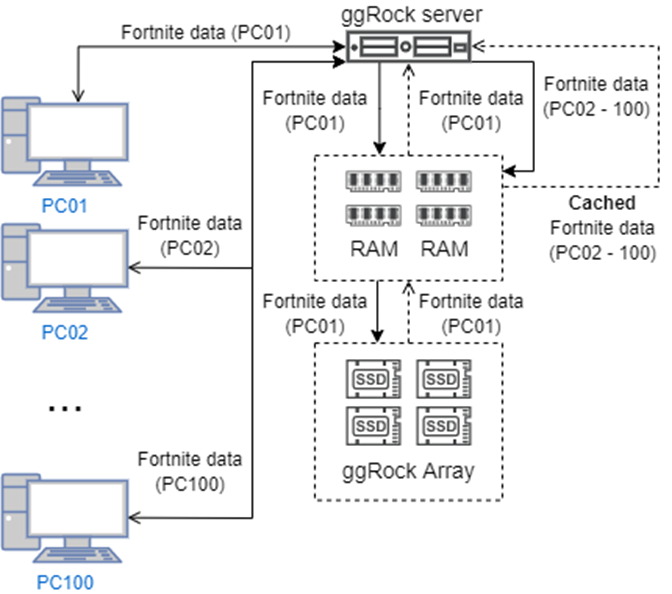
Diskless boot solutions often have RAM cache present in their configurations. This allows such services to store the most used and frequently accessed information via RAM, which works way faster compared to hard drives.
For example, if your whole esports center loads the game Fornite at the same time, the first person may have to wait a minute but the 10th would have theirs load in just 20 seconds. This is assuming that the initial delay was caused by a storage bottleneck. This is the power of RAM cache and diskless boot systems take advantage of this process.
It Can Display Higher Network Activity
Although higher network activity may seem like a cause for concern, this isn’t the case with a diskless network boot. All modern personal computers (PCs) come with a 1-gigabyte network interface as a standard, with more advanced models offering as much as 2.5 gigabytes.
In a local area network (LAN) configuration, the only time it would get saturated is when a demanding application, game, or media file is downloaded by a given IP address. Most of the time, playing video games, configuring apps, and using Windows generally will just cap the usage to 10% of the 1-gigabyte allocation.
Latency is more important for any operating system, which a diskless boot system doesn’t affect negatively.
Click here to test the ggLeap client!
ggRock Improves Performance Over Physical Hardware
The way a diskless boot system works is different from a physical hard drive installation. Many would say that using PXE boot configurations provides improved performance and capabilities than using physical hardware.
Our diskless boot system, ggRock PXE, lets you run your whole esports center floor off of a single server with RAM cache to guarantee unrivaled performance. This means that you can do away with using hard drives in all active machines since the data will be fed directly into them through ethernet cables.
ggRock lets you update any application (or several if you wanted) at a time and then apply the changes to the image so that these get shared to all machines. Furthermore, the system utilizes RAM cache to the fullest to allow users to load any video game or app even faster than an SSD.
Our ggRock PXE solution has been proven time and again to boot and load games faster than our competition. If you want to learn more about using a PXE setup for your gaming center, don’t hesitate to get in touch, sales@ggcircuit.com!